Understanding Weather Models: An In-Depth Look at the Complex Models and Algorithms Used to Predict Weather Patterns
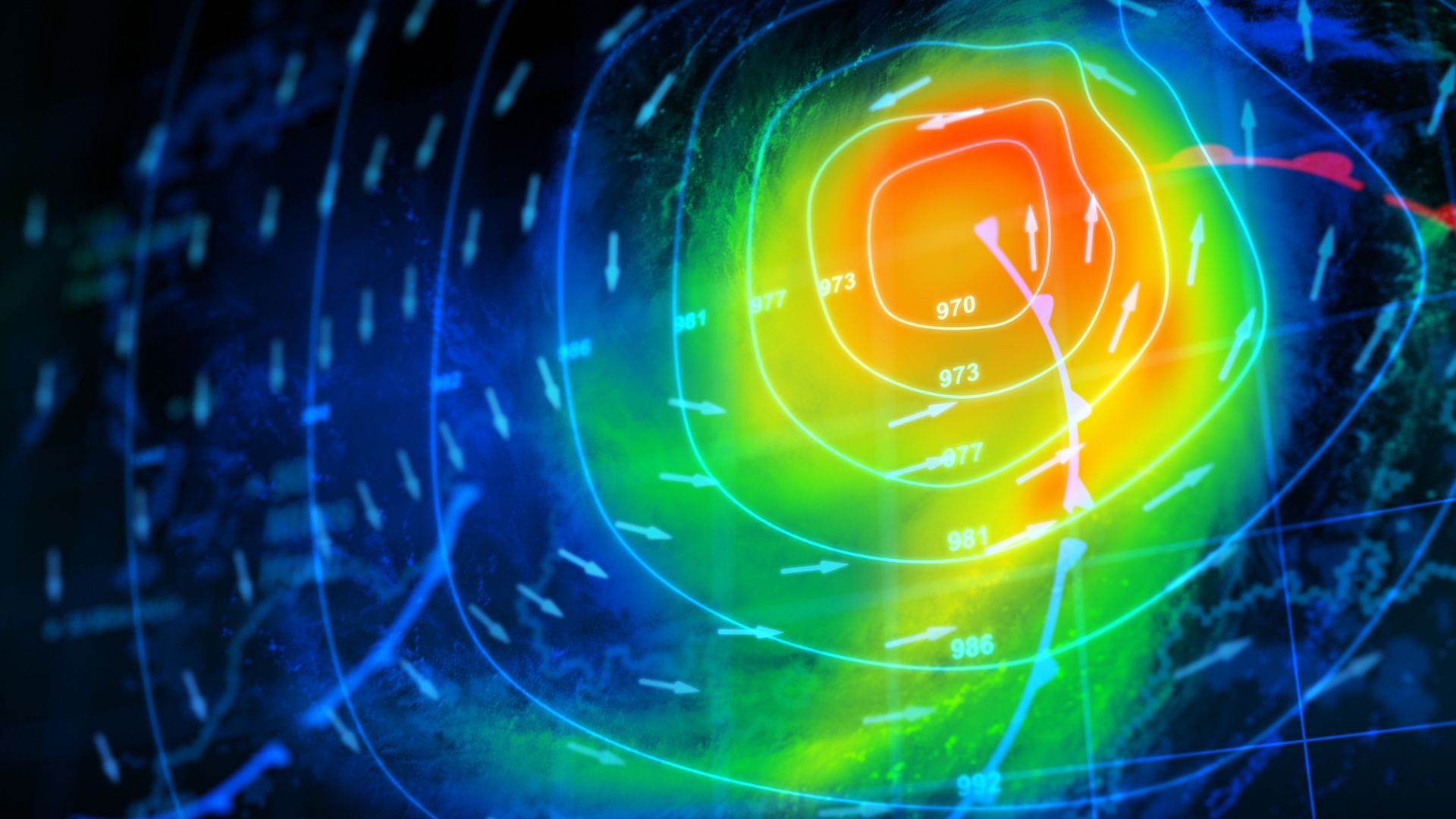
Weather prediction has become increasingly accurate thanks to the development and refinement of sophisticated weather models. These models rely on complex algorithms and vast amounts of data to forecast weather patterns with remarkable precision. At the heart of these models are numerical weather prediction (NWP) systems, which use mathematical equations to simulate atmospheric processes.
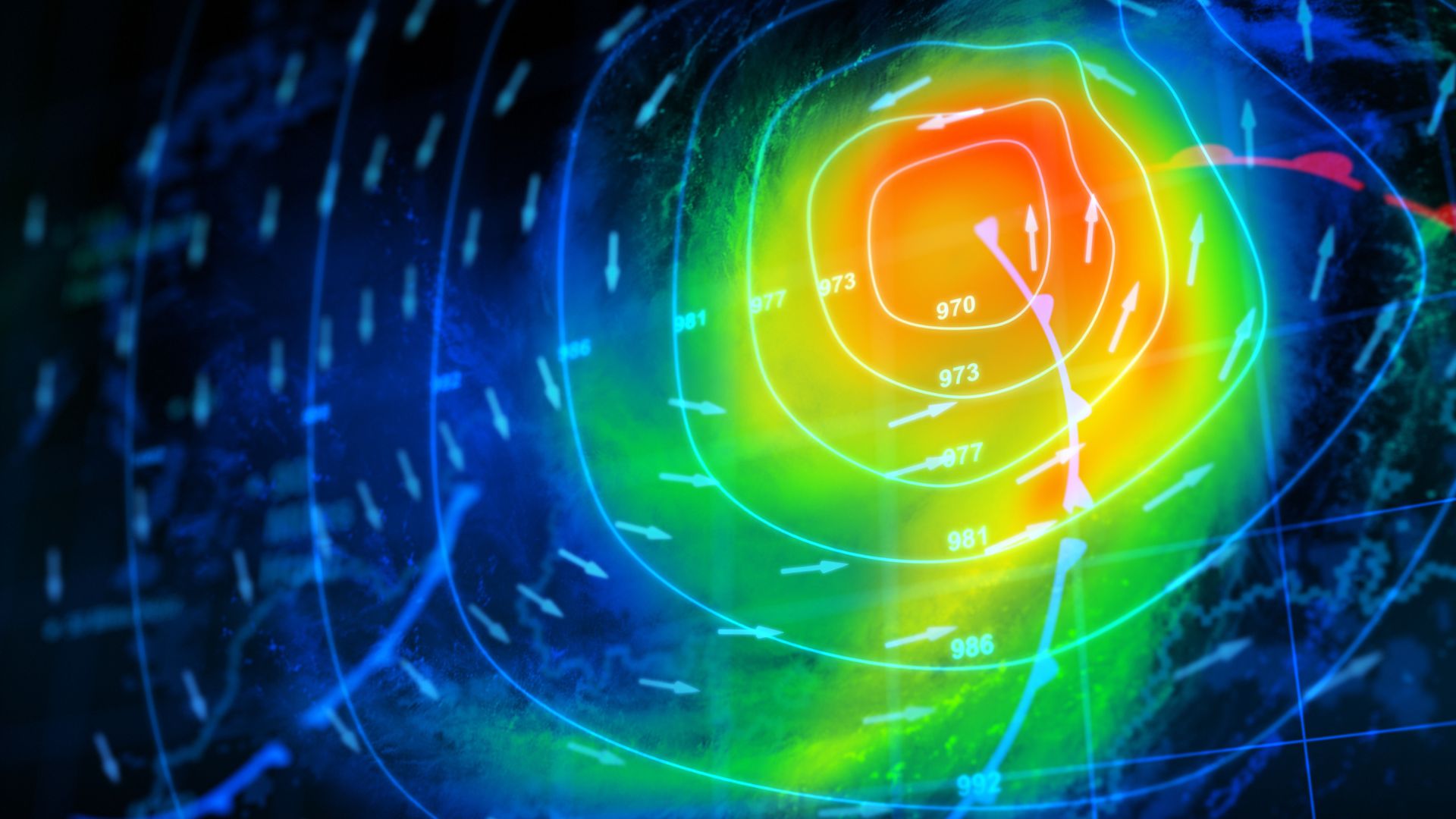
Weather models operate by dividing the Earth's atmosphere into a three-dimensional grid. Each grid cell contains information about atmospheric conditions such as temperature, pressure, and humidity. The models apply physical laws, including those governing fluid dynamics and thermodynamics, to these grid cells to predict how weather elements will evolve over time.

One of the most critical aspects of weather models is data assimilation. This process involves integrating observational data from satellites, weather stations, and radar into the model. The accuracy of forecasts heavily depends on the quality and timeliness of this data. Advanced algorithms then correct and adjust the model’s predictions based on these observations, improving their reliability.

Another key component is ensemble forecasting, which involves running multiple simulations with slightly varied initial conditions. This technique helps account for uncertainties and provides a range of possible outcomes, giving meteorologists a better understanding of potential weather scenarios.

Weather models are continually refined and updated to incorporate new data and improve their algorithms. As computational power increases, these models become more detailed and accurate, enhancing our ability to predict weather patterns and prepare for various weather events.

In summary, weather models are intricate systems that combine mathematical equations, observational data, and advanced algorithms to forecast weather. Understanding these models helps us appreciate the complexity and accuracy behind the weather forecasts we rely on daily.




